Social media has become such a constant presence in many of our lives that it's hard to imagine a world without it. In just a few short decades, social media has evolved immensely, and shows no sign of slowing down.
But when exactly did social media start? And what were those early beginnings like?
Today we'll explore the history of social media, its evolution, and its potential for the future.
Key Points:
- Understanding Social Media
- A Brief History Of Digital Communication
- The Pre-Social Media Era
- Blogs And User Generated Content
- The Impact Of Social Media
- The Economic Influence
- Ethics & Privacy Concerns
- Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Social Media

Since the advent of the internet, social media has emerged as a revolutionary force, altering the way people communicate, share information, and interact globally. It started with the birth of platforms like SixDegrees in 1997, which allowed users to create profiles and connect with others.
As the new millennium arrived, so did Friendster and Myspace, evolving the concept of virtual community-building further by making user profiles more personalized and interactive. The big breakthrough, however, came in 2004 with the launch of Facebook. Designed to connect university students, Facebook gradually expanded its network worldwide, becoming a ubiquitous part of our lives.
Following Facebook, Twitter ushered in the era of microblogging, making real-time public conversation a global phenomenon. Later, Instagram and Snapchat reshaped visual communication, promoting the culture of photo and video sharing. The evolution continued with LinkedIn professionalizing the social media space and TikTok revolutionizing short-form video content.
Today, social media is not just a communication tool but a potent influencer of public opinion, consumer behavior, and global trends. It has become the zeitgeist of the digital age, reshaping the dynamics of our society, from politics and business to culture and personal relationships.
A Brief History of Digital Communication

Social media history is filled with stories of change and innovation. The social media landscape has evolved immensely since the early social media platforms, shifting from basic email to social media sites where users create online communities with just the click of a button.
The following timeline is a testament to the rapid evolution of digital communication, continually shaped by technological innovations and societal needs.
1960s - ARPANET
The groundwork for digital communication was laid with the development of ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network) by the US Department of Defense. It was the first network to implement the protocol suite TCP/IP, which became the technical foundation of the modern Internet.
1971 - Email
Ray Tomlinson sent the first network email in 1971, creating a new way for people to communicate quickly over long distances.
1980s - Usenet and BBS
Bulletin Board Systems (BBS) and Usenet newsgroups emerged, enabling users to download files and discussions. This was a precursor to modern internet forums and social networks.
1990 - World Wide Web
Sir Tim Berners-Lee proposed the concept of the World Wide Web, leading to the first web browser and website in 1991. This revolutionary step opened the floodgates for digital
communication.
1997 - SixDegrees
The first social media site, SixDegrees, was launched, offering users the ability to create profiles and friend others.
2000s - Social Media Boom
This period saw the rise of platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, and YouTube, each shaping digital communication in unique ways and reaching audiences on an unprecedented scale.
2010s - Mobile Communication
With the advent of smartphones and tablets, digital communication became ubiquitous. Apps like WhatsApp, Snapchat, and Instagram transformed the way we share messages, images, and videos thanks to the popularity of mobile devices.
This era also introduced the concept of social media influencers.
2020s - AI and Virtual Reality
As AI and VR technologies continue to evolve, they're set to redefine digital communication, offering immersive and personalized experiences.
The Pre-Social Media Era
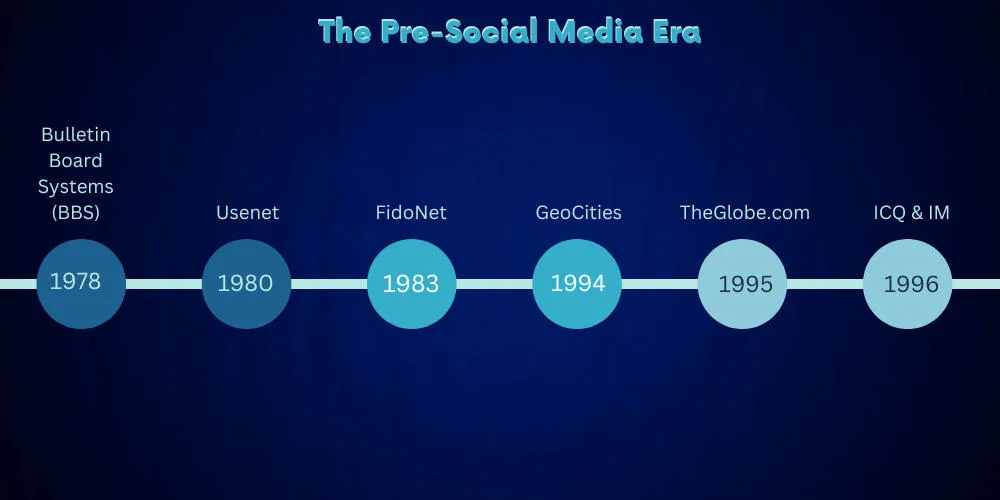
Let's take a deep dive into the early origins of the social media platform that we know today: the online community.
These early digital communication platforms set the stage for the social media revolution, pioneering concepts such as user-generated content, online communities, and real-time communication.
1978 - Bulletin Board Systems (BBS)
The precursor to modern internet forums, BBS allowed users to connect to a system using a terminal program, download files, read news, and exchange messages. The first BBS, created by Ward Christensen and Randy Suess, was a simple system for locals in Chicago to share software.
1980 - Usenet
Conceived by two Duke University students, Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis, Usenet was a worldwide distributed discussion system where users could post and read messages, akin to a public bulletin board. This represented a significant step towards global digital communication.
1983 - FidoNet
FidoNet was another significant early network that connected BBSes, allowing them to exchange personal messages and files. It became popular for its ease of use and ability to work over simple dial-up connections.
1994 - GeoCities
One of the first platforms allowing users to create their own websites, GeoCities was a critical precursor to the user-generated content that defines social media. Users could build a 'homestead' in a 'neighborhood' that corresponded to their interests.
1995 - TheGlobe.com
This website allowed users to customize their own internet experience, publish personal content, and interact with others. TheGlobe.com was one of the first platforms to incorporate the social interaction aspect that has become the bedrock of social media platforms.
1996 - ICQ and Instant Messaging
ICQ was an instant messaging client that set the stage for real-time, one-on-one communication over the internet, a feature now ubiquitous in almost all social media platforms.
Blogs and User Generated Content

Initially known as "weblogs", blogs paved the way for user-generated content. Any recognizable social media site that you use today is the direct result of these early blogs!
Before blogs, the internet was a one-way street: users consumed content published by websites, and interaction with anyone on these sites was limited.
With the advent of blogs, a sense of community, reflection, and an environment of dialogue was fostered and encouraged.
Early platforms like LiveJournal and Blogger allowed users to published their thoughts without the need for any coding skills - for the first time, anyone could be a digital publisher, creating a huge paradigm shift in digital communication.
Blogging gradually evolved from personal diaries to an endless variety of content types including how-to blogs, political blogs, business blogs, and more.
The emergence of WordPress in 2003 provided even more features and tools for creating and managing blogs, making the process more accessible to the wider public.
During this time, the concept of user-generated content began to form with the launch of Wikipedia in 2001. On Wikipedia, users create and edit content collaboratively. This marked a critical turning point, showing that users were not just consumers but valuable contributors and creators of digital content in their own right.
YouTube's arrival in 2005 was a game changer, taking user-generated content to an entirely new level by democratizing video content creation which, until then, was the domain of professionals.
Today, YouTube is the second most-used search engine and the largest platform for user-generated video content!
The Dawn of Social Media: SixDegrees and Friendster
SixDegrees and Friendster are often cited as the first social media platforms, and for good reason.
Launched in 1997, SixDegrees allowed users to create profiles and list friends. Unfortunately, it was ahead of its time and wasn't able to maintain consistent user engagement.
Friendster entered the playing field in 2002 and quickly gained millions of users, pioneering features like the "circle of friends" and profile customization.
Thanks to these early social media pioneers, future social networking sites were able to flourish and experiment with ideas that would eventually shape the social media landscape.
The Rise of MySpace: The Music-Loving Social Media Giant
In the early 2000s, MySpace emerged as a leading social media platform, particularly loved by musicians and their fans.
Launched in 2003, MySpace allowed users to customize their profiles, share music, and connect with friends, amassing millions of users within just a few years.
Its popularity among indie artists and bands for sharing their music set it apart, contributing significantly to the democratization of the music industry.
Facebook: Changing the Face of Social Media Forever
In 2004, Facebook arrived, forever altering the trajectory of social media. Initially a network for Harvard students, it soon expanded to other universities, and eventually to anyone with an email address.
With its user-friendly interface, innovative features like the news feed, and focus on real-world connections, Facebook became a social media giant, setting new standards for online social interaction.
Twitter: The Birth of Microblogging
In 2006, Twitter introduced a new form of social media communication: microblogging.
By limiting posts to 140 characters, it encouraged brevity and real-time conversation, offering a public platform for anyone to share their thoughts instantly.
Twitter quickly became a go-to source for real-time news, trending topics, and social activism.
The Advent of Instagram: Revolutionizing Photo Sharing
Instagram, launched in 2010, revolutionized the way people shared photos.
With its simple, mobile-first design, and features like filters and hashtags, Instagram made photo-sharing social, fun, and accessible, establishing visual content as a key element of social media communication.
LinkedIn: Professional Networking Reimagined
LinkedIn, launched in 2003, brought a professional twist to social networking. It allowed users to create professional profiles, connect with colleagues and peers, and share industry-related content.
Today, LinkedIn is the go-to platform for professional networking, job searching, and business-to-business marketing.
YouTube: Democratizing Video Broadcasting
YouTube, launched in 2005, democratized video broadcasting by enabling anyone to upload, share, and discover videos.
It transformed video content from a one-to-many broadcast medium to a many-to-many social medium, becoming a crucial platform for user-generated content, entertainment, education, and marketing.
Snapchat: The Power of Ephemeral Content
Snapchat hit the social media scene in 2011 with a unique proposition: ephemeral content.
By making photos and messages disappear after viewing, it introduced a more casual, spontaneous style of communication. Snapchat's Stories feature became so popular that it was later adopted by other platforms, including Instagram and Facebook.
TikTok: The Latest Social Media Phenomenon
TikTok, launched internationally in 2016, has taken the social media world by storm with its short-form, creative videos.
Its ease of use, algorithmic feed, and creative tools have made it a hit among younger audiences, emerging as a key platform for viral trends, memes, and influencer marketing.
The Impact of Social Media

Social media has profoundly shaped society and culture in countless ways, forging new paths for communication, information exchange, and relationship-building.
The global proliferation of platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram has fundamentally altered how we connect and interact, often blurring the line between our online and offline lives.
Social media's most profound impact is arguably its democratization of communication. By allowing everyone to broadcast their thoughts and experiences, it has given a voice to individuals and communities that might otherwise remain unheard.
It has also made it easier for people to stay connected with family and friends, share personal milestones, and explore shared interests with like-minded individuals across the globe.
Moreover, social media has significantly influenced popular culture, often setting trends and propelling conversations on everything from fashion and music to politics and societal issues.
Viral challenges, memes, and hashtags can rapidly garner global attention, reflecting and shaping public sentiment. User-generated content, once seen as secondary to professional content, has found a massive platform in social media, often driving trends and cultural shifts.
The influence of social media on political discourse and activism is undeniable. Platforms like Twitter have become vital for political campaigning, policy discussions, and citizen activism.
Movements like #BlackLivesMatter and #MeToo have used social media to rally support, share stories, and effect change on a global scale.
However, alongside these benefits come concerns. The spread of misinformation, online harassment, and the pressure to present an idealized version of one's life are significant issues that social media users face on a daily basis. Balancing the power and potential of social media with these challenges is an ongoing societal conversation, shaping and reflecting our evolving digital culture.
The Economic Influence

Social media platforms have become powerful economic entities, influencing various sectors, from advertising and retail to job recruitment and financial markets. Their rise has reshaped business models, consumer behavior, and market dynamics in profound ways.
In advertising, social media platforms have revolutionized how businesses reach consumers. Targeted advertising, enabled by user data collected by these platforms, allows businesses to reach specific demographics with personalized ads.
Influencer marketing, another social media-born phenomenon, leverages the popularity of social media personalities to promote products and services.
E-commerce has also been transformed by social media. Platforms like Instagram and Facebook have integrated shopping features, blurring the line between social networking and online shopping. This fusion of social interaction with consumer behavior has given rise to social commerce, a growing segment of the e-commerce market.
Social media's economic influence also extends to the job market. Platforms like LinkedIn provide a digital space for job seekers and employers, facilitating professional networking, job postings, and personal branding. Digital business cards complement this online presence, allowing professionals to share their contact information quickly and seamlessly across social platforms.
However, the economic power of social media platforms raises concerns about market concentration and data privacy. The monetization of user data, a cornerstone of social media's business model, has raised ethical and regulatory questions, challenging societies and governments to reassess existing regulatory frameworks.
Ethics & Privacy Concerns
In the age of social media, ethics and privacy concerns have taken center stage. As platforms collect vast amounts of data to enhance user experiences and target advertisements, issues around data privacy, consent, and security have emerged.
One key concern is the collection and use of personal data. Social media platforms often have access to a wealth of user data, from basic demographic information to user interests, behaviors, and networks. While this data drives the free services we enjoy, it's often used for targeted advertising, raising concerns about privacy and informed consent.
Cyberbullying and harassment are also significant ethical issues in the social media sphere.
Platforms struggle to balance freedom of speech with the need to protect users from harm, creating ongoing debates about the role of moderation and algorithmic bias.
Conclusion
Social media is an ever-evolving landscape filled with possibilities and revolutionary ideas. However, as it continues to evolve it also presents challenges - from privacy concerns to the spread of misinformation, to cyber bullying and digital harassment.
As users, it's essential to navigate these changes thoughtfully, taking into account our needs and the benefits of social media with its potential for harm.
The future of social media is something we as users can actively shape through our individual choices, the policies we advocate for, and the methods we use to connect and share content.
Frequently Asked Questions
When did social media first start?
Many cite the launch of SixDegrees in 1997b as the dawn of social media.
Was social media a thing in 2004?
Yes, in 2004 Facebook was launched but social media had been around for almost a decade already.
Was social media a thing in 2005?
Yes, in 2005 Facebook was already 1 year old.
Did social media exist in 2008?
Social media has existed in its most recognizable form since 1997.
Did social media exist in 2011?
Yes, in 2011 Snapchat was launched following the success of Facebook and Instagram.
What is the oldest social media ever?
SixDegrees is the oldest official social media site - it's been around since 1997.


